1918
This press release presents the results regarding purchasing power in Romania compared to the member states of the European Union. The data were calculated by Eurostat in December 2023, both based on consumer prices collected by participating countries for a common nomenclature of comparable goods and services, selected as representative of consumption patterns in the 36 European countries, as well as based on GDP expenditure items and other basic information transmitted in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1445/2007.
Price Level Indices for Final Household Consumption Compared to the EU Average
Price level indices express how many units of the same currency are needed to purchase an identical volume of goods and services in different countries, for each group of goods and services.
In 2022, for consumer goods and services comprising final consumption, 100 euros are paid at the EU level, with the two extremes being 149 euros in Denmark and 59 euros in Romania and Bulgaria, respectively.
The lowest price level for consumer goods and services comprising final household consumption among the member states was recorded in 2022 in Bulgaria and Romania, being 41% lower than the EU average, followed by Poland (39% below the EU average).
In 2022, among the member states of the European Union, the highest price level for final household consumption was recorded in Denmark (49% above the EU average), followed by Ireland (42% above the EU average), Luxembourg (37% above the EU average), and Finland (26% above the EU average).
Price Level Indices for Major Groups of Goods and Services
According to Eurostat's Press Release*), Romania is the cheapest member state for the "Food and Non-Alcoholic Beverages" group (72%), followed by Poland (73%), while at the opposite end are Denmark and Luxembourg, having the highest price levels for this group of products (121%).
Bulgaria has the lowest price level for the groups "Alcoholic Beverages and Tobacco" (66%), "Clothing and Footwear" (80%), and "Housing, Water, Electricity, Gas, and Other Fuels" (38%), followed by Poland, for the groups "Alcoholic Beverages and Tobacco" (73%) and "Housing, Water, Electricity, Gas, and Other Fuels" (39%).
Denmark has the highest price level for products in the "Clothing and Footwear" group (133%), while Ireland is the most expensive EU country for products in the "Alcoholic Beverages and Tobacco" (216%) and "Housing, Water, Electricity, Gas, and Other Fuels" (195%) groups.
Bulgaria and Romania have the lowest price levels among EU countries for the group "Furniture, Household Equipment, and Current Maintenance of the Dwelling" (71%).
Hungary remains the cheapest member state for the "Transport" group (70%), followed by Poland for the "Recreation and Culture" group (62%), while Bulgaria has the lowest price level for accommodation and restaurant services (50%).
Luxembourg has the highest price level for "Furniture, Household Equipment, and Current Maintenance of the Dwelling" (128%) among the member states, while Denmark is the most expensive country in the EU for the "Transport" (129%), "Recreation and Culture" (143%), and accommodation and restaurant services (154%) groups.
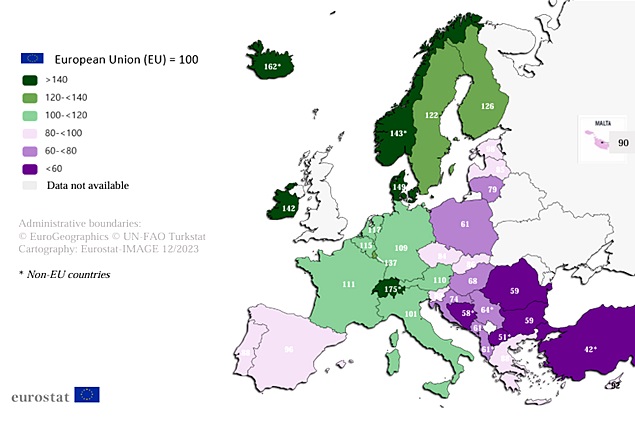
Volume Indices of Gross Domestic Product per Inhabitant
Volume indices of Gross Domestic Product per inhabitant calculated based on Purchasing Power Parity show that Romania, together with Hungary, registers the same value of the GDP volume index per inhabitant, calculated based on PPP, and stands at 76% of the EU average.
The lowest Gross Domestic Product per inhabitant value in 2022 was recorded in Bulgaria, 38% below the EU average.
The highest level of GDP per inhabitant in the European Union was recorded in Luxembourg, exceeding the EU average by 156%. This is partially explained by the fact that a large number of foreign citizens have a significant share in the total workforce of the country and contribute to GDP, but are not part of the resident population.
(The European Comparison Program (ECP) was initiated in the 1970s as part of the International Comparison Program (ICP) and aims to compare real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) – level and structure.)





