1661
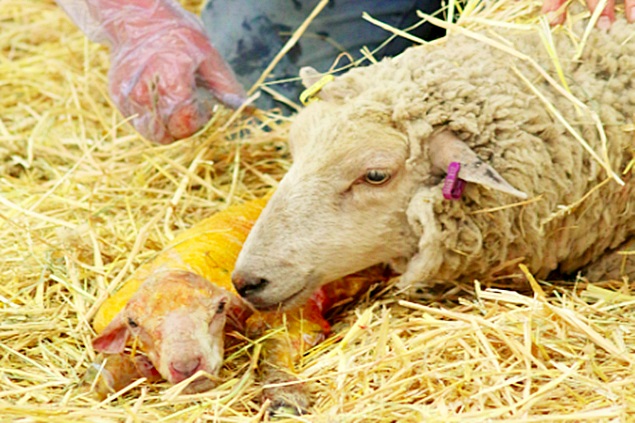

During the sheep lambing period, zootechnical specialists advise farmers to adhere to a set of hygiene rules to ensure proper results, as follows:
Throughout the gestation period, the sheep must be carefully supervised, avoiding overcrowding in shelters, as well as at the entrance and exit of shelters or pens.
Feeds should be of the highest quality, avoiding moldy feeds, and two weeks before lambing, ensiled or pickled feeds should be removed from the diet.
Cold water should not be administered to avoid abortions.
In the last part of gestation, the wool around the tail and udder should be sheared to ensure good hygiene for suckling and/or milking. This action must be done very carefully, considering the advanced gestation and the possibility of causing abortions through hitting.
Preparing shelters for lambing: creating a compartment for pregnant ewes, a maternity ward, and a compartment for lambs. Individual lambing boxes should be arranged in the maternity ward, with dimensions of 1.2/0.6 – 0.8 m, maintaining a temperature of 18-20°C, disinfecting, whitewashing, and changing bedding daily after population.
Lambing symptoms: 1-2 days before lambing, the abdomen drops, the udder enlarges and becomes turgid, and the vulva swells. Approaching lambing, the ewe becomes restless, seeks a secluded place, lies down, and gets up frequently. When these symptoms are observed, the ewe should be introduced into the lambing box. The expulsion of the fetus takes 30-40 minutes, and in the case of twin births, the second fetus is expelled 15-20 minutes after the first. The placenta is expelled within the first 3 hours after lambing, and uterine involution occurs in approximately 30 days.
Caring for lambs after birth: after expulsion, the lamb is given its first care – removing mucus from the head, mouth, and nostrils, cutting the umbilical cord 4-5 cm from the abdomen if it has not ruptured during lambing, and disinfecting it with iodine tincture.
Subsequently, the lamb is left for approximately 20-30 minutes to be licked by the ewe, which is equivalent to a massage that activates blood circulation. After this, the ewe is prepared for the first nursing by cleaning the udder and milking the first streams of colostrum.
Feeding lambs in the first days after birth: after 8-10 days of age, combined feeds and high-quality alfalfa hay can be administered in specially arranged locations. In the case of twin lambs, when the ewe does not have milk or has died, farmers will place the lambs with surrogate ewes, born approximately at the same time, or resort to bottle-feeding with cow's milk.
The "newborn lamb" period lasts from 0 to 7 days, the "middle lamb" period lasts from 8 to 30 days, and the "grown lamb" period lasts from 31 to 65 days. The compartment for housing ewes with grown lambs is arranged in common boxes, ensuring approximately 1.6 m² for each ewe with a lamb.
Weaning lambs – is done according to breed, age, body weight, and the purpose of the lambs (for replacing the flock, raising, fattening, or slaughter during the Easter period). It is recommended that weaning be gradual, over 4-5 days.
The lambs will be separated from the mothers overnight, and in the morning, the ewes will be milked, with the lambs being left with the mothers for a few hours during the day in the following days, thus reducing weaning stress. After periods when the lambs are separated from the ewes, the ewes are milked.
When weaning lambs abruptly, they show signs of discomfort, weaken, and sometimes become ill. During weaning, the feed ration is supplemented with high-quality feed. (Photo: Freepik)